SimplySQS: Create special quasi-random structures (SQS) with ATAT mcsqs in interactive interface for input files and output analysis of SQS
Access the application online here: simplysqs.com (or at https://atat-sqs.streamlit.app/)
Workflow overview
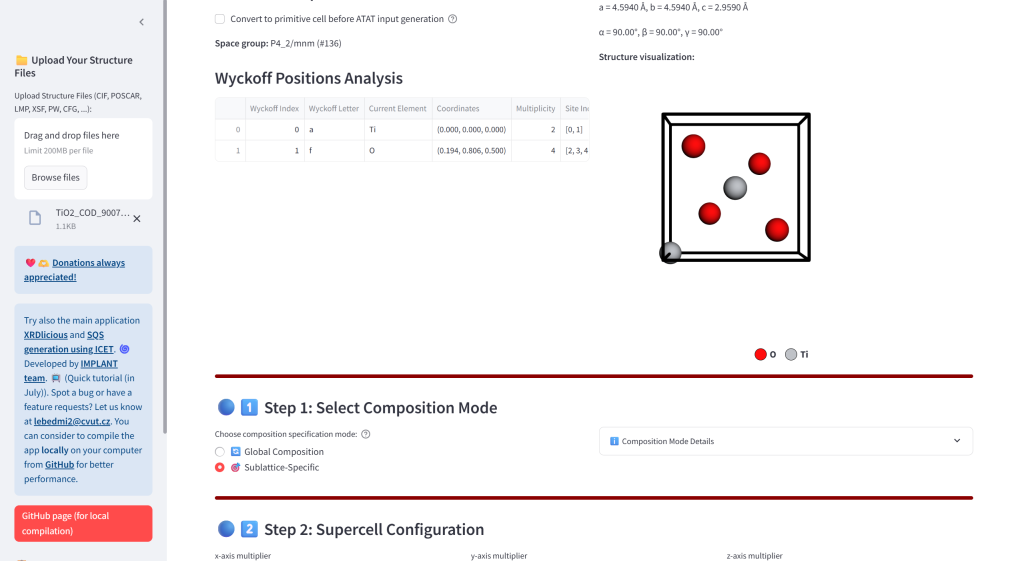
- Upload crystal structures or retrieved them from implemented search interface in MP, AFLOW, and COD databases.
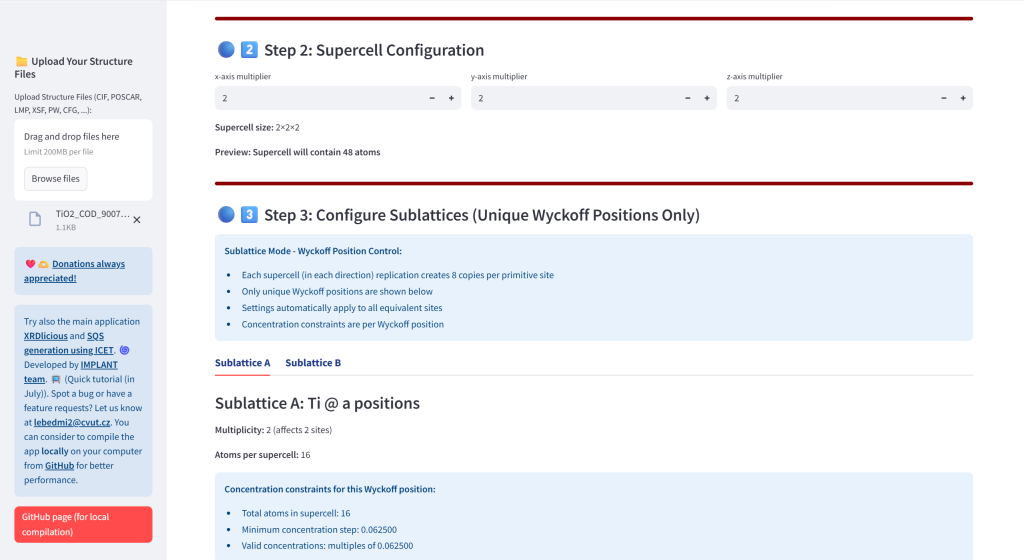
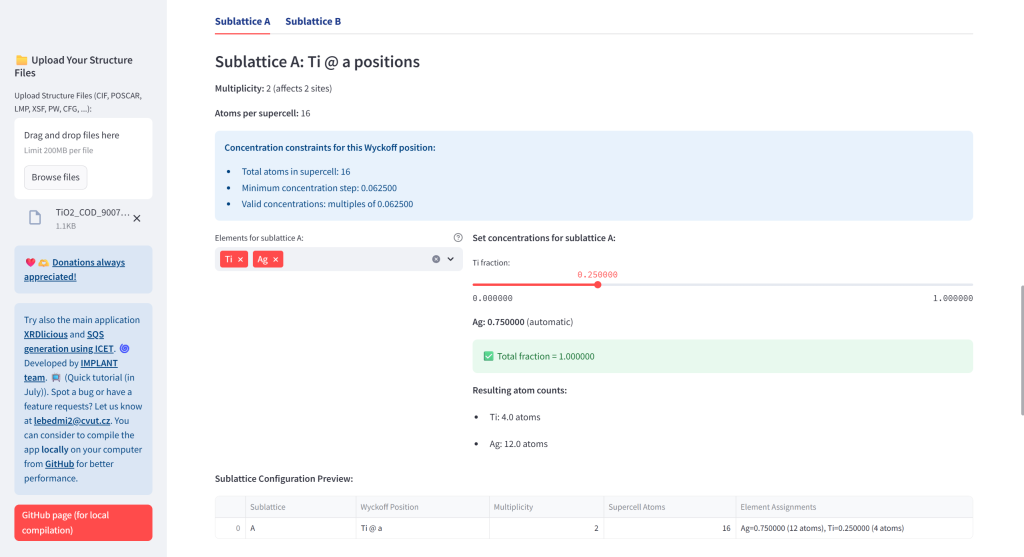
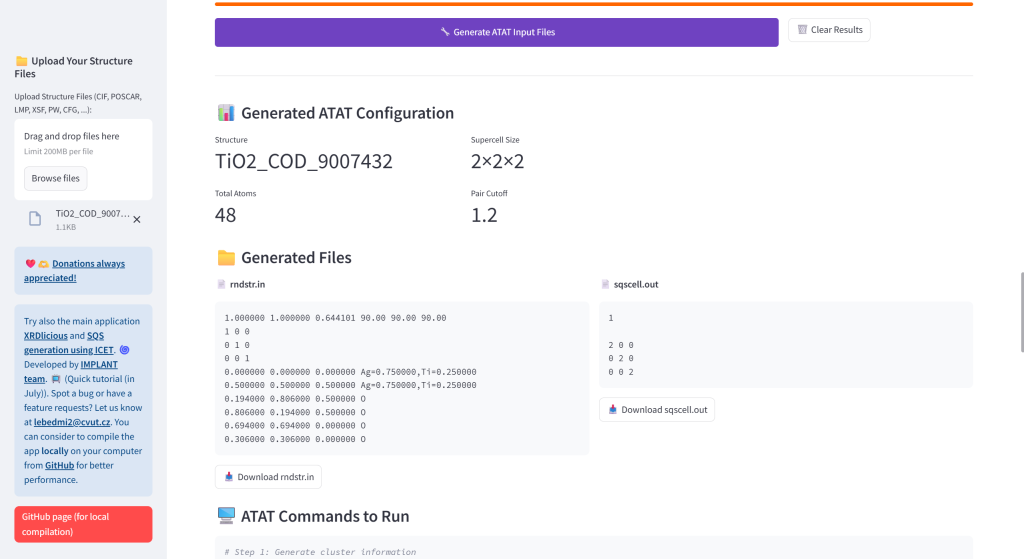
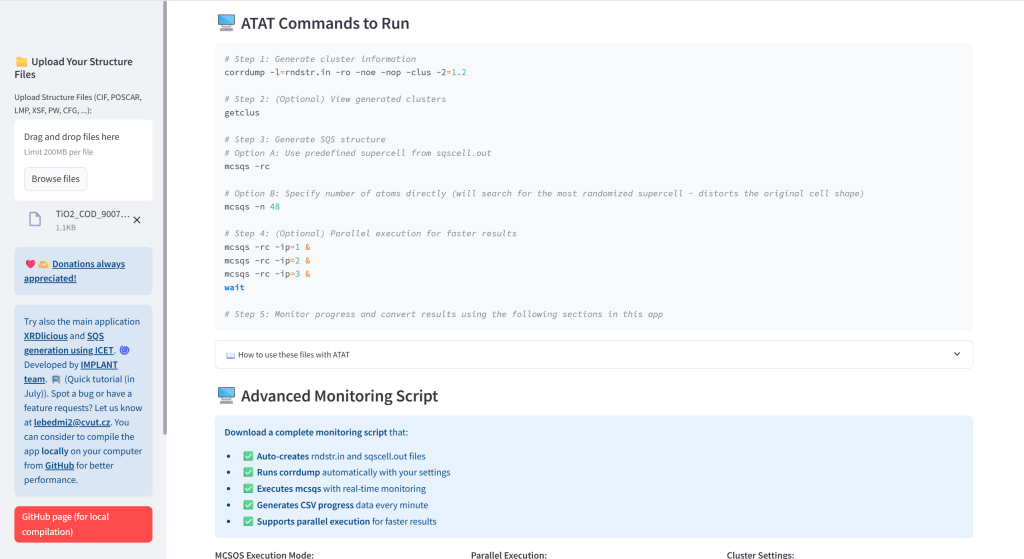
- Generate ATAT Input Files: Create rndstr.in and sqscell.out files with global or sublattice-specific composition control. The concentrations are automatically recalculated for the achiavable concentrations given the total number of atoms in supercell.
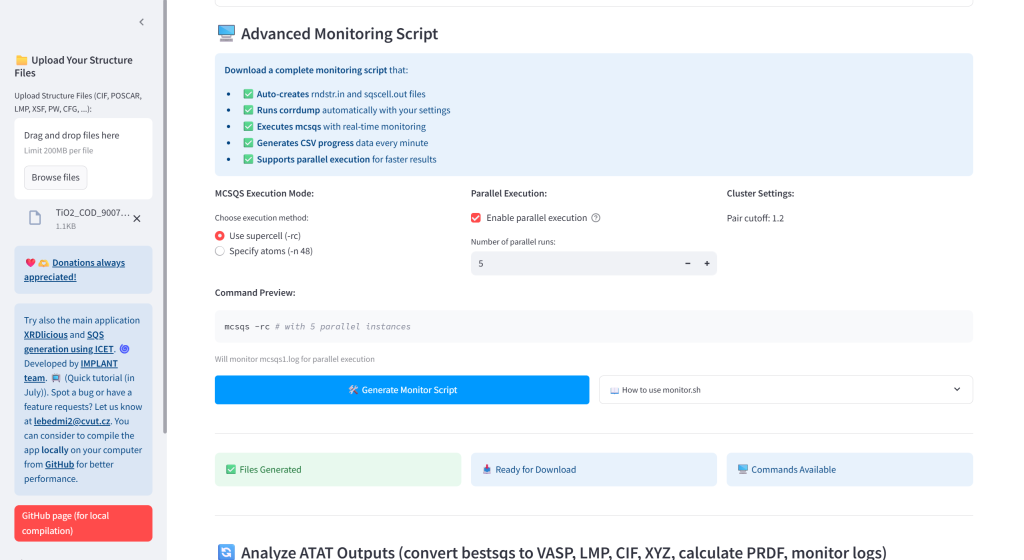
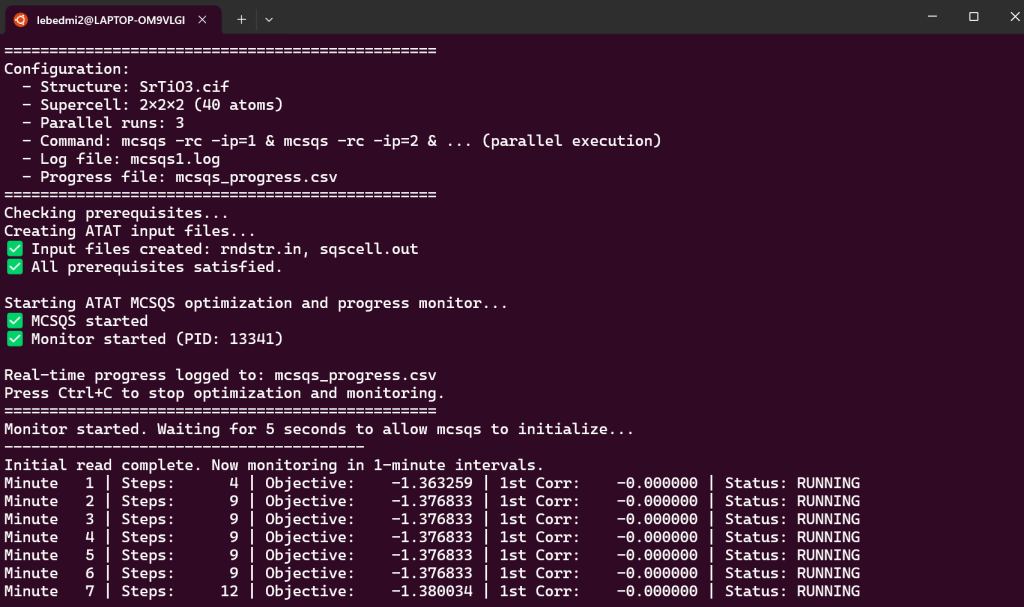
- Generate complete bash script that will create the rndstr.in and sqscell.out and run the ATAT mcsqs with improved monitoring and creating the mcsqs_progress.csv
- Generate complete bash script to automate the SQS search across a range of compositions for a binary alloy system.
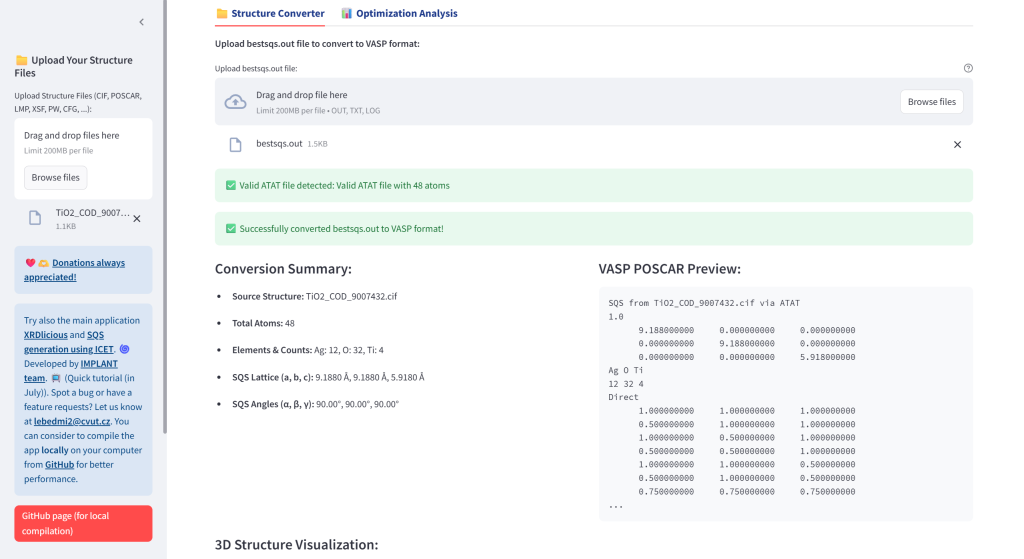
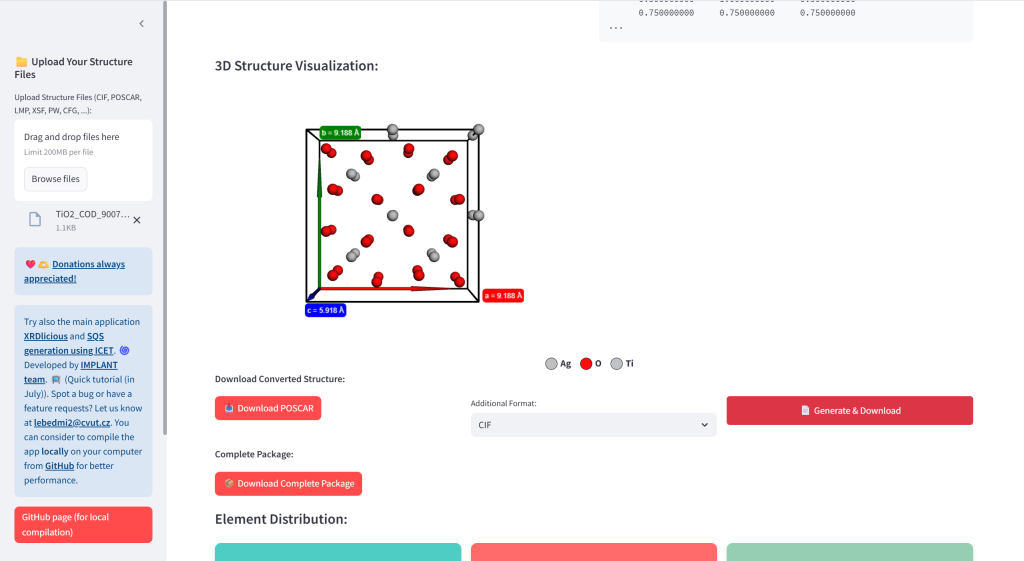
- Convert ATAT Output: Transform bestsqs.out files to VASP, CIF, LAMMPS, and XYZ formats with 3D visualization
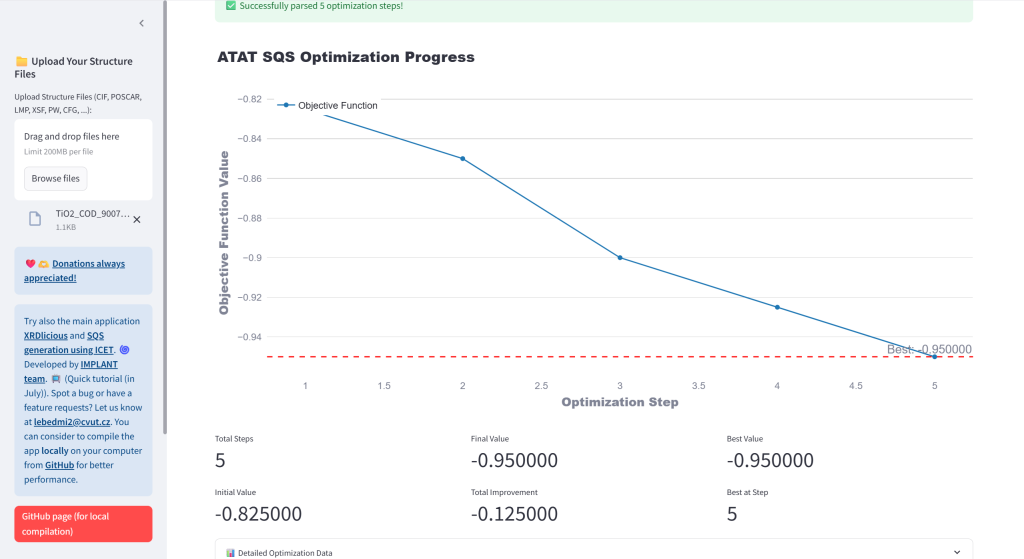
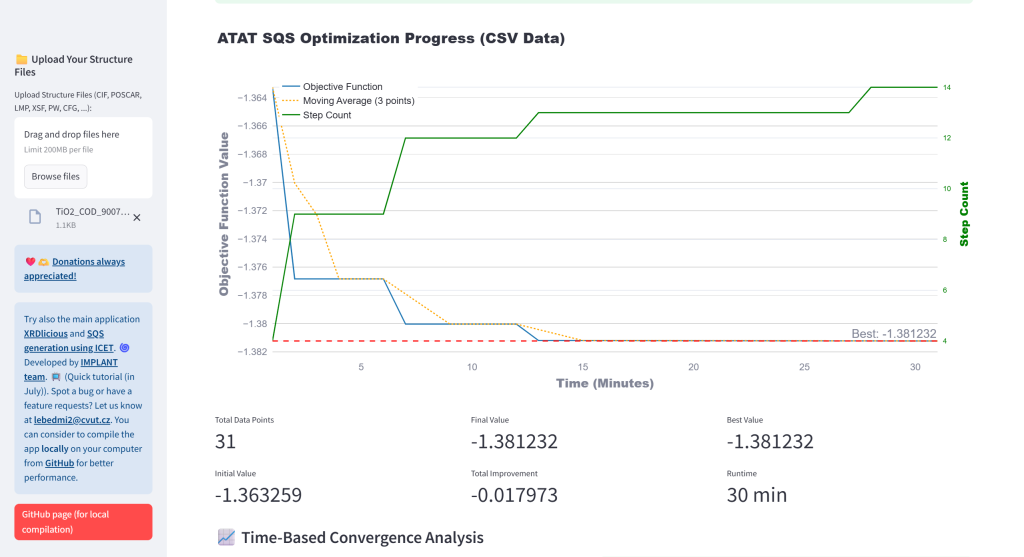
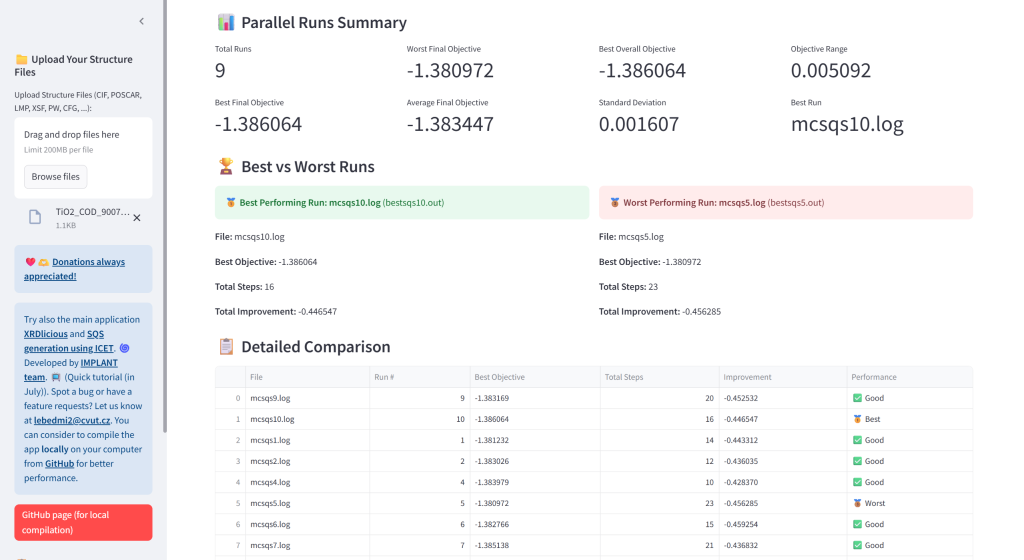
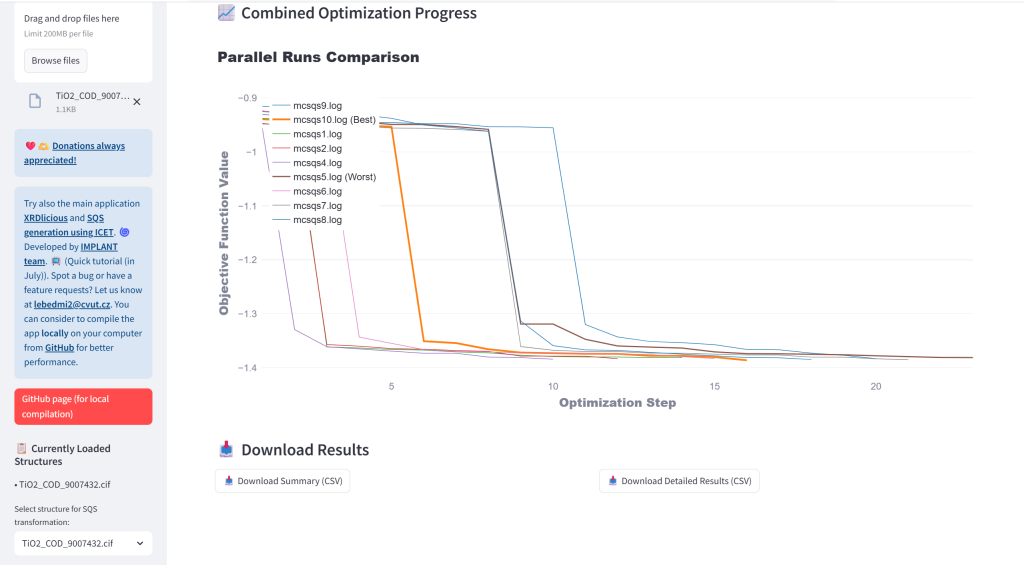
- Monitor Optimization: Analyze ATAT convergence from log files (mcsqs.log or at once for parallel run with mcsqs1.log, mcsqs2.log, …) and CSV time progress file (mcsqs_progress.csv) data with interactive plots and main information. For parallel run, it will automatically identify the best performing optimization
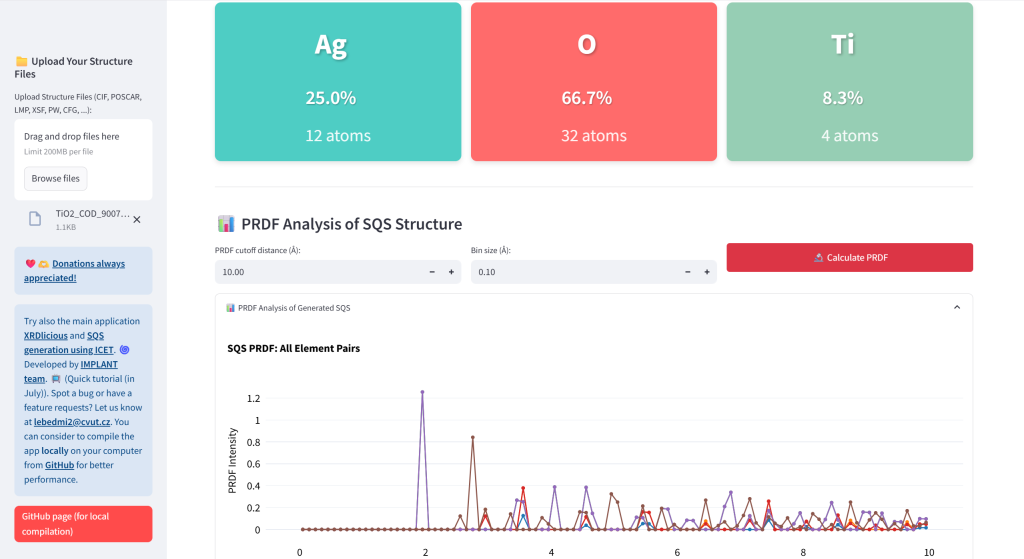
- Calculate PRDF: Compute Partial Radial Distribution Functions for SQS
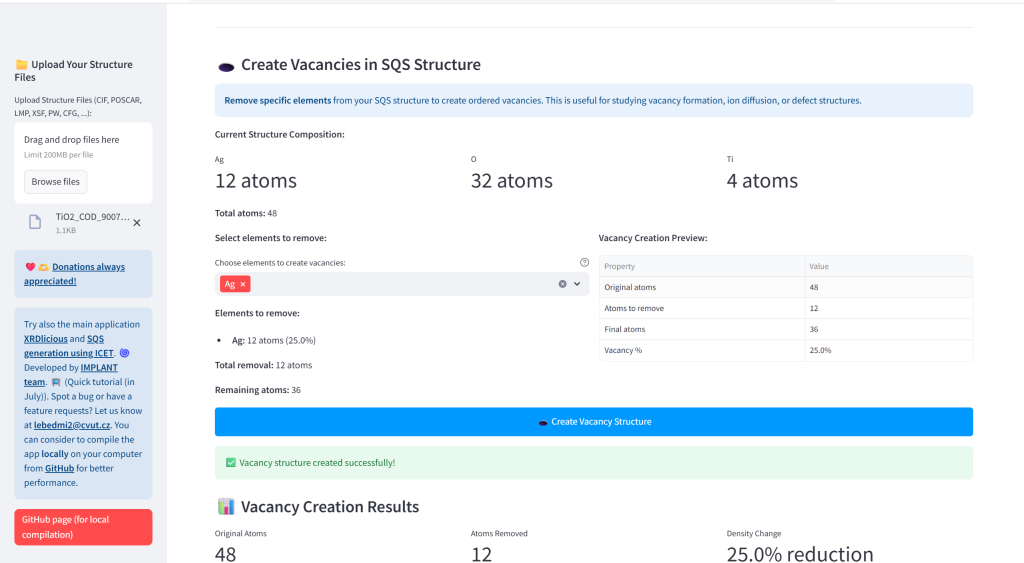
- Create Vacancy Structures: Generate ordered defects by selectively removing specific element from the SQS
Workflow